- Home
- Cleaning
Cleaning
Alkaline cleaners are excellent at eliminating stubborn, moist soils when applied via spraying or dissolved in warm water. They operate through various mechanisms:
Saponification: Alkaline cleaners facilitate the removal of oils, fatty acids, and greases by transforming them into water-soluble compounds.
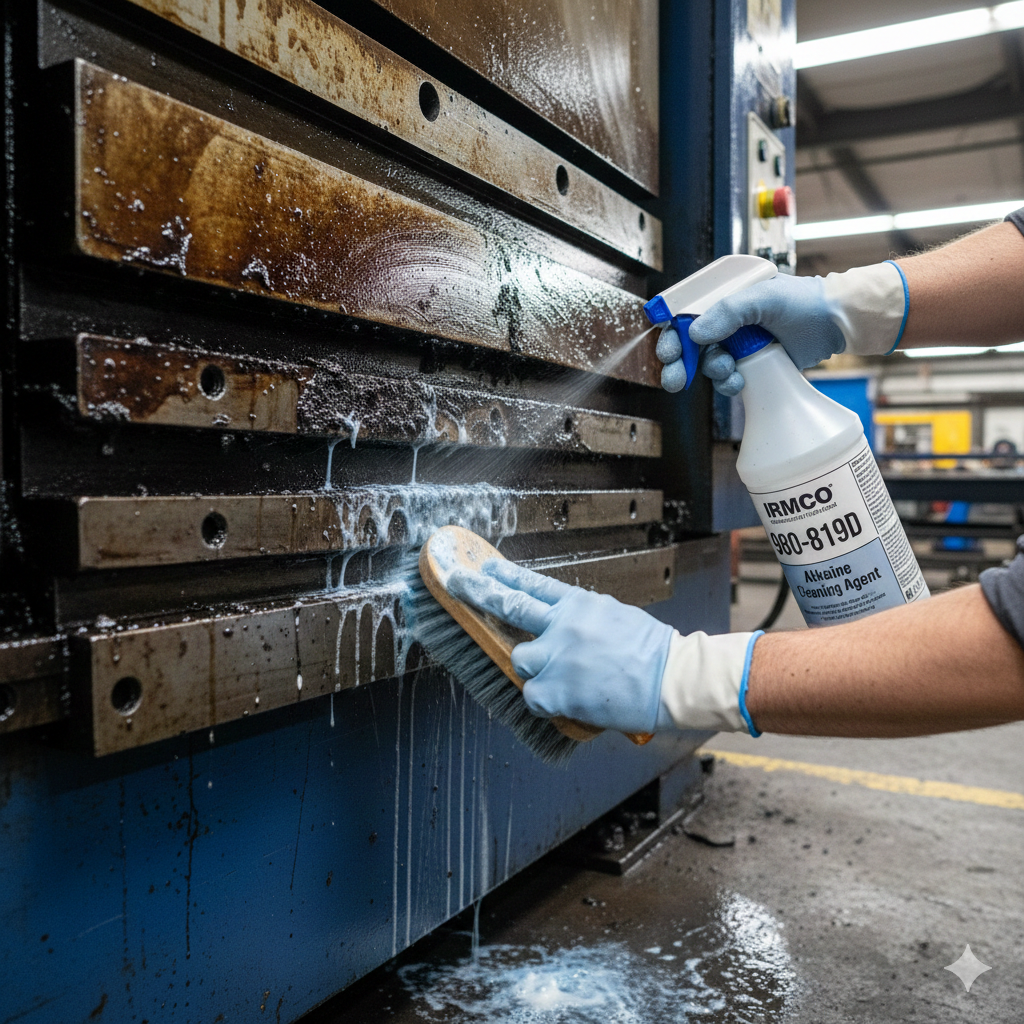
Successful metal cleaning depends on using alkaline cleaners, which are primarily made up of phosphates, silicates, and caustic compounds. These cleaners have a stable blend of active agents on their surfaces, making them highly efficient at removing contaminants. They are not only among the most effective options available, but they are also notable for their affordability, especially in automated cleaning processes. Alkaline cleaners are excellent at eliminating stubborn, moist soils when applied via spraying or dissolved in warm water.
They operate through various mechanisms:
- Saponification: Alkaline cleaners facilitate the removal of oils, fatty acids, and greases by transforming them into water-soluble compounds.
- Solvent Action: This feature enables alkaline cleaners to effectively dissolve surface oils on metals.
- Emulsification: Alkaline cleaners suspend oil particles, facilitating their easy rinsing from the surface.
- Detergency: Active wetting agents reduce surface tension on metals, enhancing the penetration and displacement of soil.
- Deflocculation: The cleaning solution disperses contaminants into very fine particles, suspending them in the solution.
While alkaline cleaners are well-known for their ability to fight dirt, selecting the appropriate type and using the correct amounts is important to ensure optimal efficacy in industrial settings.
Saponification
One of the fundamental chemical reactions in alkaline cleaning is saponification. This reaction involves the hydrolysis of fats and oils (triglycerides) into glycerol and fatty acid salts (soap) in the presence of an alkali (such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide). Alkaline cleaners break down fats and oils by converting them into water- soluble soap molecules, which can then be easily rinsed away with water.
Emulsification
Alkaline cleaners contain surfactants, which are molecules with both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions. These surfactants help to emulsify oils and grease by surrounding oil droplets with their hydrophobic tails, while their hydrophilic heads interact with water molecules. This emulsification process disperses the oil or grease into tiny droplets, allowing them to be suspended in water and washed away.
Dispersing and Chelating Agents
Alkaline cleaners often contain dispersing and chelating agents, which help prevent the redeposition of dissolved soils and contaminants onto surfaces. Dispersing agents work by keeping soil particles suspended in the cleaning solution, preventing them from reattaching to the surface being cleaned. Chelating agents bind to metal ions present in soils, preventing them from forming insoluble complexes that could lead to staining or surface damage.
pH Adjustment
The high pH of alkaline cleaners plays a crucial role in their cleaning effectiveness. The alkaline environment helps to break down and dissolve acidic soils, such as mineral deposits, rust, and scale. Additionally, the high pH facilitates the saponification reaction by providing the necessary conditions for the hydrolysis of fats and oils.
Complexation
Some alkaline cleaners contain complexing agents that form complexes with metal ions present in soils. These complexes prevent them from reacting with other compounds or interfering with the cleaning process. These complexes are water-soluble and can be easily rinsed away with the cleaning solution.
Benefits of Using Alkaline Cleaners
Effective Contaminant Removal
Alkaline cleaners are more effective in removing solid contaminants than organic chlorinated solvents. This efficacy is attributed to their alkaline nature, which allows them to break down and emulsify various types of soils and contaminants, including grease, oils, fats, and other organic substances.
Heavy-Duty Cleaning
Alkaline cleaners excel at tackling tough stains, soils, and contaminants, making them ideal for heavy-duty cleaning tasks. They are commonly used in industrial facilities, commercial kitchens, automotive workshops, and other environments where thorough cleaning is required.
High pH
The high pH level of alkaline cleaners helps to neutralise acidic substances and contaminants, such as oils, grease, and food residues. This makes them particularly effective for cleaning surfaces that have been soiled with acidic substances.
Compatibility
Alkaline cleaners are generally compatible with various cleaning equipment, including pressure washers, steam cleaners, and scrubbing machines. This makes them easy to integrate into existing cleaning processes and equipment.